Posted by Spycor LLC on Nov 21st 2025

INDUSTRIAL-GRADE HEPA FILTERS are not an accessory; they are the uncompromising foundation of professional environmental remediation. When your project involves capturing highly hazardous, ultra-fine particulates like respirable crystalline silica, dangerous mold spores, aggressive asbestos fibers, or infectious bioaerosols, a standard air filter is a liability. You need specialized, heavy-duty HEPA filtration—the critical component engineered for robust air scrubbers and demanding industrial settings.
This guide focuses on the essential role of specialized, industrial HEPA filters designed primarily for powerful, continuous air scrubbing in professional and remediation settings. If your operation requires an air purification system where capturing the most elusive, hazardous particulates is absolutely critical, understanding the technology and applications of these filters is key to both compliance and protection.
Defining the Gold Standard: What Makes a
Filter Truly “HEPA”?
The term HEPA stands for High-Efficiency Particulate Air. It is not just a brand name; it is a stringent performance standard established by the U.S. government.
For a filter to be certified as HEPA, it must be capable of removing at least 99.97% of particles that are 0.3 micrometers (µm) in diameter. This size, known as the Most Penetrating Particle Size (MPPS), is the most difficult to capture. By efficiently trapping particles at this size, the filter also easily captures both larger and smaller particulates.
The Mechanism of Ultimate Filtration
Unlike simple mesh filters that only act as a sieve, a true industrial-grade HEPA filter uses a complex, dense mat of randomly arranged fibers (usually fiberglass) to capture particulates through three distinct physical mechanisms:
-
Interception: As an airflow particle passes close to a fiber, it is physically snagged and held onto the fiber.
-
Impaction: Larger, heavier particles cannot follow the air stream around the fibers and slam directly into the fiber, adhering to its surface.
-
Diffusion: The smallest, lightest particles (like some bioaerosols) move randomly and erratically due to collision with gas molecules. This chaotic motion increases their likelihood of striking and becoming permanently trapped by a fiber.
This combination ensures a level of air purity that is essential for controlled environments, allowing these filters to capture hazardous particulates as small as the viruses and bacteria that constitute bioaerosols.
Why Standard HVAC Filters Fail the Professional Test
Many facility managers attempt to use high-MERV (Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value) filters in their standard HVAC systems, believing they offer enough protection. While a high-MERV filter (like a MERV 14 or 15) is excellent for general indoor air quality, it is fundamentally inadequate for professional remediation settings involving highly toxic materials.
MERV vs. HEPA in Critical Environments:
-
MERV 13/14: Generally captures less than 95% of particles in the 0.3–1.0 µm range. This is the range where dangerous contaminants like mold spores and respirable silica dust reside.
-
HEPA (99.97%): Guarantees the capture of at least 99.97% of particles at the MPPS.
In a situation involving asbestos removal or a massive mold colony, releasing even 5% of the fine, hazardous fibers back into the environment is completely unacceptable and a major regulatory violation. Only the rigorous standard of a heavy-duty HEPA filter can provide the necessary capture efficiency for legal compliance and worker safety.
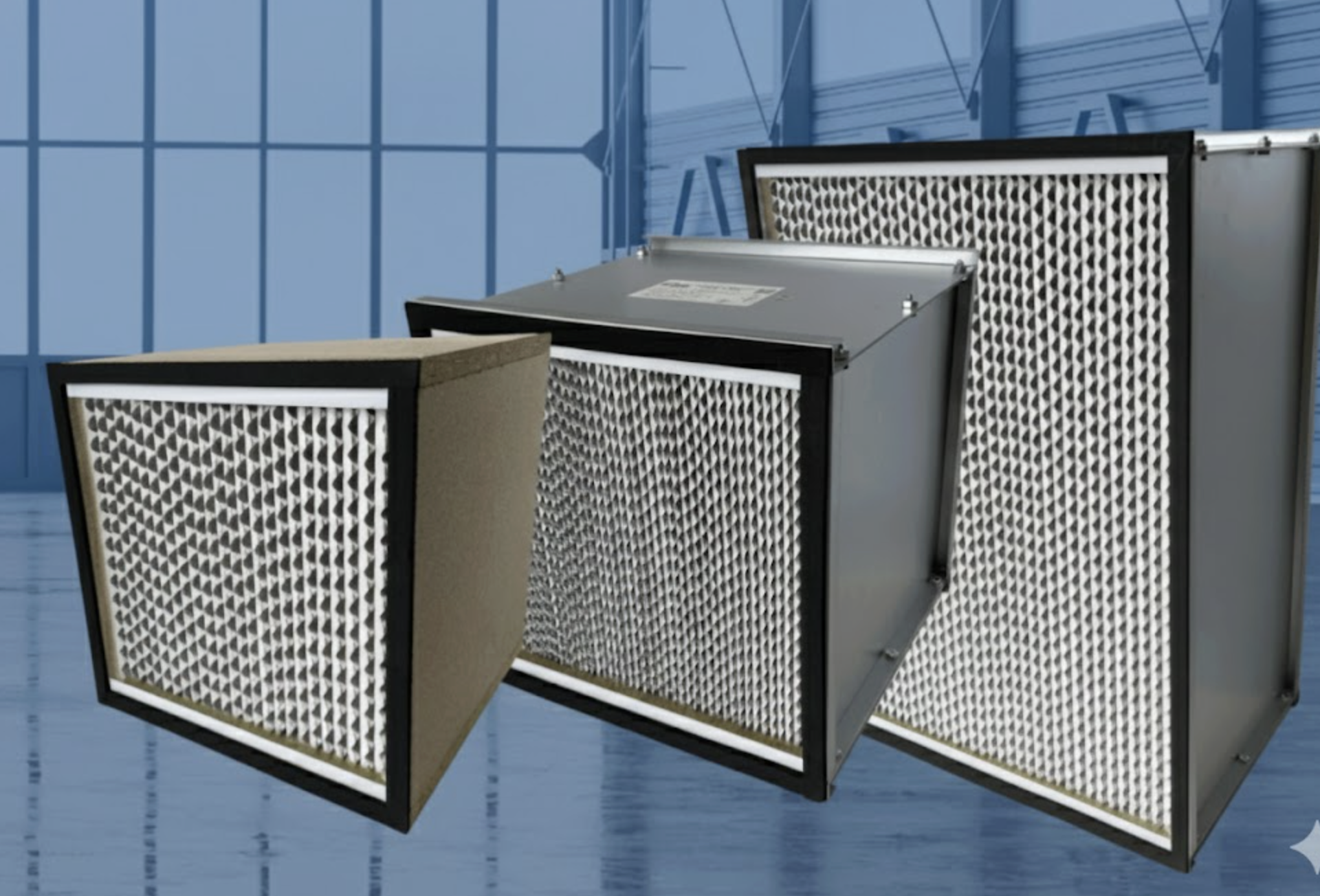

Essential Applications for Industrial HEPA
Filters
The core of professional air purification lies in robust equipment like Negative Air Machines (NAMs) and certified industrial vacuums. Here are the professional settings where these specialized filters are the bedrock of safety and regulatory adherence.
1. Asbestos and Lead Abatement
When dealing with materials that contain asbestos fibers or lead paint dust, the risk of serious, long-term health damage is extreme. Asbestos fibers are notorious for being easily aerosolized and can lead to diseases like asbestosis and mesothelioma.
-
The Critical Role: In abatement projects, Negative Air Machines (often called air scrubbers) are mandatory. These machines use asbestos removal HEPA filters to maintain negative pressure within the work zone, preventing the escape of contaminated air. Every cubic foot of air exhausted from the work area must pass through a certified HEPA filter, trapping 99.97% of the cancer-causing fibers before the air is released into the clean environment.
-
Compliance: Using a certified HEPA filter in this context is mandated by OSHA and EPA regulations. The filter is the final, non-negotiable barrier of protection.
2. Mold and Disaster Remediation
Water damage and flooding inevitably lead to the growth of mold. Once disturbed, mold colonies release massive quantities of mold spores and mycotoxins into the air, which can cause severe respiratory and neurological issues.
-
The Critical Role: Mold remediation air scrubbers equipped with industrial HEPA filters are essential during the demolition and cleaning phases. They capture the agitated spores and airborne mold fragments, preventing cross-contamination to clean areas of the building. For certain types of toxic mold, a 99.99% HEPA filter may be preferred for added assurance.
-
Equipment Focus: This is a primary use case for high-capacity, heavy-duty HEPA filters designed to handle the high volume and moisture typical of disaster recovery work.
3. Controlling Bioaerosols in Healthcare and Labs
The control of airborne pathogens—bioaerosols—is a critical public health concern, especially in hospitals, infectious disease wards, and bio-safety labs.
-
The Critical Role: Critical environment air filtration is achieved using HEPA filtration systems to create Infectious Disease Isolation Rooms (IDIRs) or to protect ultra-sensitive processes in laboratories and pharmaceutical manufacturing cleanrooms. In these settings, HEPA filters capture airborne bacteria and viruses, ensuring a sterile environment.
-
Specialized Needs: Many of these applications require specialized HEPA filters 99.99% or even 99.999% efficient to meet the hyper-strict air purity standards of these facilities.
4. Silica and Fine Dust Control in Construction
Modern building materials and demolition methods produce massive amounts of respirable crystalline silica and general construction dust. Inhalation of these fine particulates leads to severe respiratory illnesses.
-
The Critical Role: Contractors rely on localized exhaust ventilation systems and specialized HEPA vacuums, all of which require a robust, certified filter to capture the hazardous dust at the source. The high-capacity design of heavy-duty HEPA filters allows them to handle the extreme dust loading found on active construction sites without premature failure.
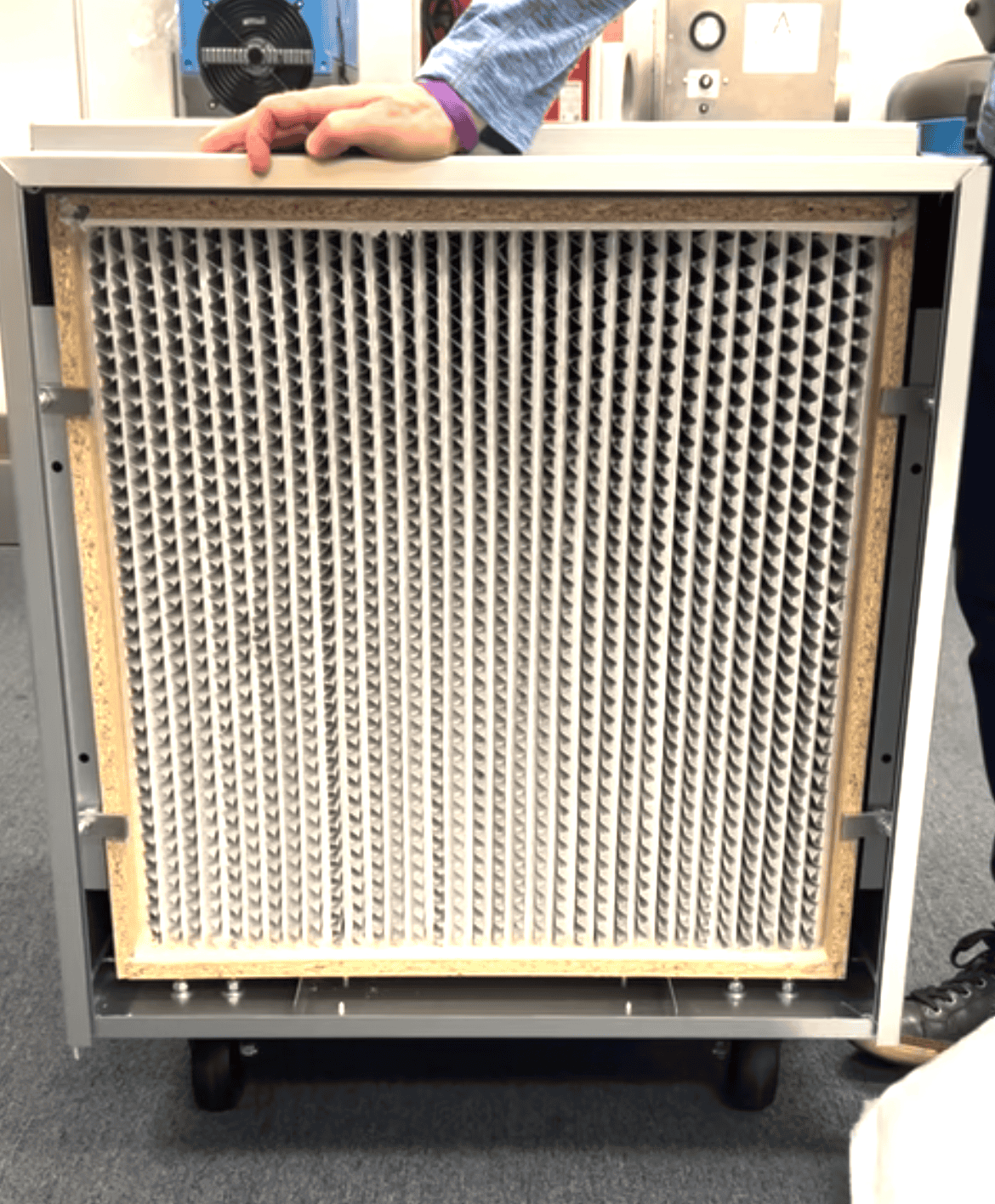
The Essential Component: Negative Air
Machine HEPA Filters
The workhorse of environmental remediation is the Negative Air Machine (NAM), often simply called an air scrubber. The function of this equipment is completely reliant on the quality and certification of its HEPA filter.
The air scrubber pulls potentially contaminated air through a series of pre-filters (to capture large debris and extend the HEPA filter life) and then forces it through the final, high-efficiency HEPA stage. This two-stage process maximizes the lifespan and effectiveness of the main filter, ensuring the integrity of the containment zone.
When looking at filters for this vital equipment, professionals must consider the construction quality, as the entire assembly—including the filter—must be robust enough to withstand the rigors of an active job site.
Choosing the Right HEPA Filter
Construction for Heavy-Duty Air Filtration
The specific HEPA filters available for industrial air filtration are engineered for durability and performance in demanding environments:
-
99.97% vs. 99.99% Efficiency: While 99.97% meets the mandated federal standard, 99.99% filters offer extra assurance for the most sensitive tasks, such as those involving highly virulent pathogens or extremely fine contaminants.
-
Wood Frame HEPA Filters: These are often used in standard-capacity air scrubbers for general remediation tasks, offering a balanced, reliable performance.
-
Metal Frame HEPA Filters: Built for maximum structural integrity and harsh environments. The metal frame prevents warping, making them ideal for high capacity units and use in potentially moist conditions, providing a longer, more reliable service life in heavy-duty air filtration applications.
-
High Capacity HEPA Filters: These filters feature a deeper, pleated media pack, allowing them to hold a significantly larger volume of contaminants before the filter needs replacement. This translates to fewer filter changes, reduced operational downtime, and sustained high airflow on projects with extreme dust loading.
Compliance and Quality Assurance:
Certification and Testing
For professional use—especially in regulated fields like asbestos and lead abatement—it's not enough to simply buy a HEPA filter; it must be proven to meet the standard. The accountability starts with the manufacturer.
-
DOP/PAO Testing: Before being shipped, high-quality industrial HEPA filters are individually tested using a highly refined aerosol (historically DOP, now often PAO or comparable media) to ensure the filter media and the filter housing are free of leaks and that the 99.97% (or higher) efficiency rating is met. This leak-checking process confirms the filter’s integrity.
-
Certification: Always look for suppliers that provide filters certified with an individual test report, guaranteeing the performance of the filter for your project. This documentation is often a requirement for final project sign-off and safety audits by regulatory bodies. Failing to have this documentation can lead to costly project delays and penalties.
The investment in a tested, certified heavy-duty HEPA filter is an investment in regulatory compliance and the success of the remediation project itself.
The Ultimate Investment in Safety and Professionalism
For operations demanding absolute purity—from mitigating infectious disease risks to legally and safely removing carcinogenic materials—there is no substitute for a specialized, industrial-grade HEPA filter. These filters represent the ultimate insurance policy for your employees, your clients, and your business reputation. They are the essential link that transforms a powerful negative air machine into a compliant, life-saving tool for heavy-duty air filtration.
To ensure your equipment is running at maximum efficiency and compliance, always choose filters engineered for the extreme demands of professional remediation.
Order Now to protect your workers, your clients, and your environment with certified, heavy-duty HEPA filters from the industry leader, spycor.com.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About
Industrial HEPA Filters
What is the difference between a 99.97% and a 99.99% HEPA filter?
A 99.97% HEPA filter captures at least 99.97 out of every 10,000 particles at the MPPS (0.3 µm). A 99.99% HEPA filter (often called a Near-ULPA filter) captures 99.99 out of every 10,000 particles. While the difference seems small, the 99.99% option is used when requirements are hyper-critical, such as in certain pharmaceutical cleanrooms or highly sensitive biohazard isolation rooms, offering an additional layer of assurance against the smallest bioaerosols.
How do I know when my Negative Air Machine HEPA Filter needs to be replaced?
In air scrubbers, the filter should be replaced when the airflow drops significantly or when the pressure differential across the filter (measured by a manometer or gauge on the machine) reaches the manufacturer's specified limit. A higher pressure drop indicates that the filter is loaded with particulates and requires replacement to maintain effective airflow and capture efficiency. Replacing pre-filters regularly will significantly extend the life of the main HEPA filter.
Can I vacuum asbestos fibers or mold spores with a regular shop vac?
Absolutely not. A regular shop vacuum or even a non-HEPA industrial vacuum will draw in the fine, hazardous particles and then blow them directly back into the air—a process called blow-by. This causes dangerous contamination. All vacuuming for asbestos removal or aggressive mold remediation must be done using a specialized HEPA-filtered vacuum that is certified to the 99.97% standard.
Are wood frame HEPA filters safe for use in damp environments like water damage sites?
While wood frame filters are commonly used and effective, a metal frame HEPA filter is generally preferred for environments with high humidity or moisture, such as post-flood disaster recovery. The metal frame is less susceptible to warping or degradation from moisture exposure, which ensures the filter media remains properly sealed and prevents air from bypassing the filter, a critical concern in heavy-duty air filtration.
What is the benefit of a High Capacity HEPA Filter?
High Capacity HEPA Filters feature a deeper media pack and more pleated surface area. This allows the filter to hold significantly more dust and debris before reaching the maximum acceptable pressure drop. For jobs with extremely high levels of airborne particulates (e.g., heavy demolition or extensive dust containment projects), high-capacity filters reduce the frequency of filter changes, saving both time and money on the job site while maintaining continuous, peak performance.


